IIoT Solution for SDGs: Food Traceability for Smart Supply Chain Management Enabled by SenseCAP LoRaWAN in Shenzhen, China
By Ye Seong SHIN 3 years agoBaoneng Cold Chain Warehouse Project introduces how Seeed’s SenseCAP series is helping food industry players to manage their products intelligently and safely to reduce time, resources, and wastes, and to contribute to the UN’s SDGs 12, 3, 9 and 17.
Project Name: Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse
Project Deployment Location: Shenzhen, China
Targeted Industry Type: Food
Project Partner(s): 
In the era of Decade of Action towards the UN’s 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (UN, 2020), more and more people (including you and I) are gradually self-empowered, if not nudged, to make small and big changes in their un-sustainable daily life habits. One of such global trends includes sustainable food consumption, through which consumers all around the world are realizing the importance of quality and sustainable food products. Naturally, various industries have been inspired to fulfill the upsurging demand, by adopting food traceability systems.
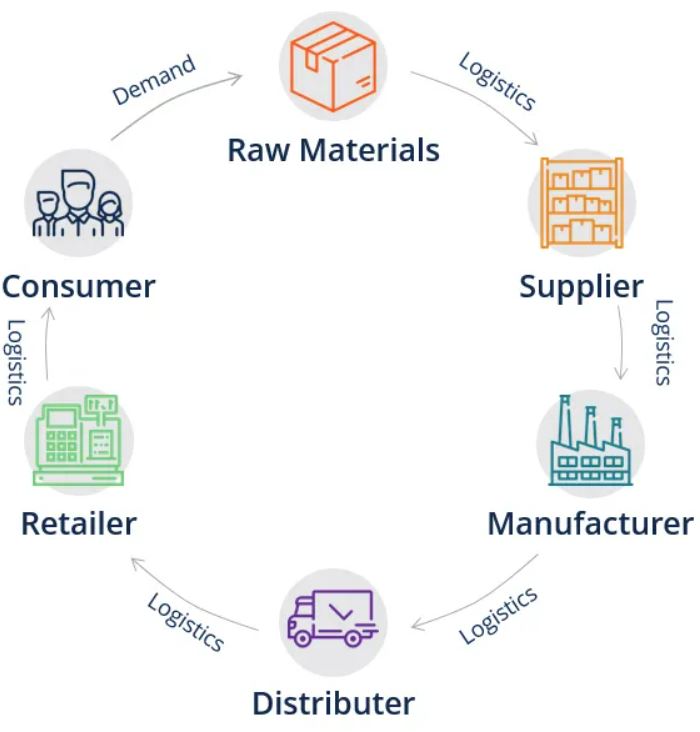
Figure 1. The Whole Supply Chain at a Glance (CFI, n.d.)
As amazing as it may sound, food traceability means the ability to track and trace movement, locality, and conditions of raw food materials, ingredients and processed products all along the whole food supply chain (Figure 1). It can minimize and prevent hazardous risks on customers’ health. Undeniably, such a tracking system provides transparent and integral evidence to multi-stakeholders – be it companies, government agencies, civil society organizations (CSOs), academia – in making well-informed decisions.
What’s the Challenge?
How to monitor and manage food materials’ safety, quality, and optimal environmental conditions throughout the whole supply chain?
What’s the Project About?
In 2021, Seeed collaborated with Baoneng Group on a food-tracking project at Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse in Shenzhen, China (Figure 2). The project has sought to observe and maintain an appropriate surrounding environment for agricultural, food, and healthcare products in the warehouse. In order to do that, Baoneng Group applied our environmental monitoring solution for this project – the SenseCAP LoRaWAN series.
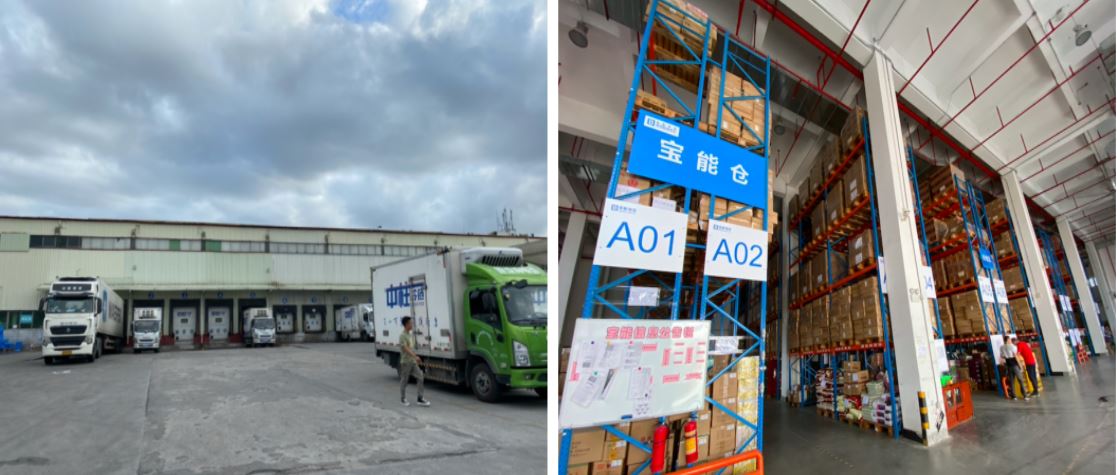

Figure 2. Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse in Shenzhen, China
Baoneng Group is a Shenzhen-based conglomerate in international logistics, urban development, and livelihood services, including quality food management. The company has a corporate culture of “combination, co-creation, and sharing”, with its mission of serving the society. Science and technology is their first engine of development, with a special focus on IoT, AI, cloud computing, big data, and blockchain. That is why, Baoneng Group has deployed our IIoT solution to promote intelligent tech ecology within their food industry.
SenseCAP is a series of IIoT products. Its LoRaWAN version is based on LoRaWAN protocol, and is deployable worldwide with multiple ISM bands. SenseCAP is encapsulated in an IP66 enclosure, making it applicable to remote sensing scenarios outdoors, like Smart Farming, Smart City, and other countless IoT application possibilities, that need low-power, long-distance, and long-term data collection features. By providing precise parameters, sensors assist warehouse managers to make accurate estimations and predictions of product quality, and remove faulty products from the market as soon as any risk factors are detected. For today’s case on Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse in Shenzhen, the deployed IIoT devices (Figure 3) include:
- SenseCAP Wireless CO2 Sensor – LoRaWAN
- SenseCAP Wireless Barometric Pressure Sensor – LoRaWAN
- SenseCAP Wireless Air Temperature and Humidity Sensor – LoRaWAN
- SenseCAP Outdoor Gateway – LoRaWAN
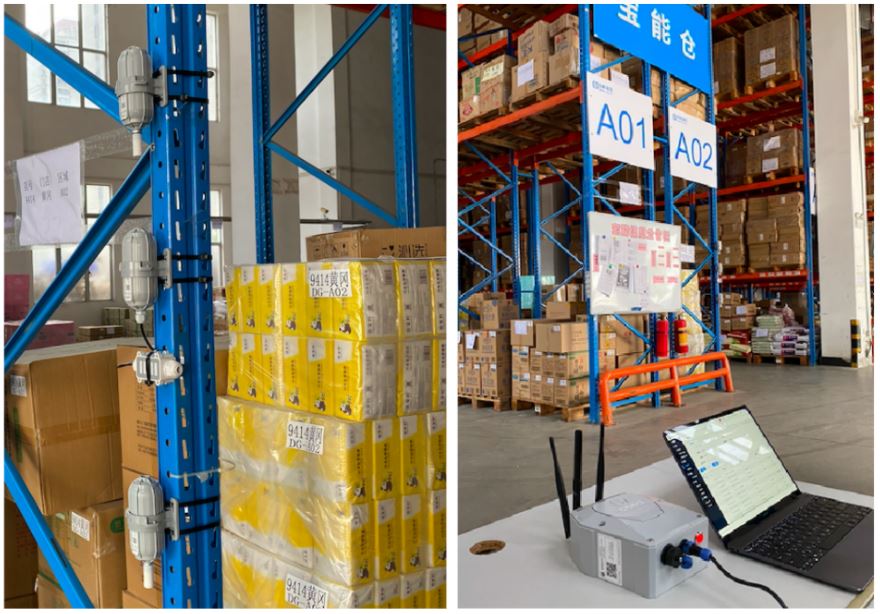

Figure 3. Seeed’s IIoT Solution Deployed in Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse
These SenseCAP devices are equipped to perform 4 main functions (Figure 5):
- The three types of SenseCAP sensors collect each parameter of air temperature, humidity, CO2, and barometric pressure inside the warehouse. Afterwards, the collected data is wirelessly transferred to the central gateway.
- Since data is transmitted to the cloud platform from the sensors and central gateway respectively, warehouse managers only need to examine the food materials’ environmental conditions on their computers. Thanks to this simplicity and convenience, they can save a lot of time and energy, because they no longer have to ramble around the big-scaled warehouse, which oftentimes, has extreme conditions (Figure 4: freezing inside the warehouse!). In this way, SenseCAP series reduces what was previously perceived to be a cumbersome procedure, curtails all types of significant costs imaginable, and improves efficiency of supply chain management.
- As the SenseCAP line supports LoRaWAN technology, it guarantees the wireless sensors to work over long distances with low-power consumption. Moreover, they are robust enough to work in severe environmental conditions for many years.
- To your surprise, only one gateway is needed to be connected with hundreds of sensors in multiple warehouses, and its actual transmission distance is up to 2 km, including obstacles. In every 5 minutes, the warehouse managers can obtain data from the SenseCAP LoRaWAN sensors. What’s even better, SenseCAP line’s batteries contain a relatively long lifespan, with the average lifespan ranging from 3 to 8 years.
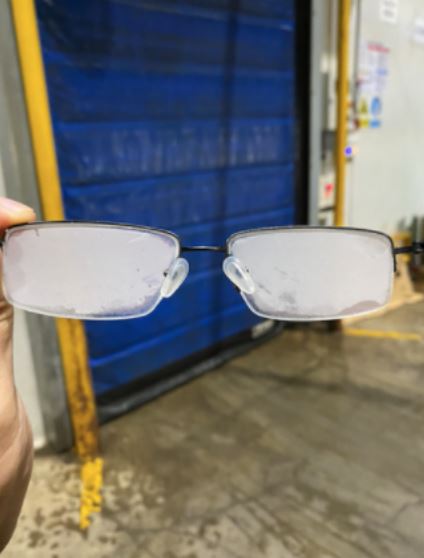

Figure 4. Glasses After Visiting Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse
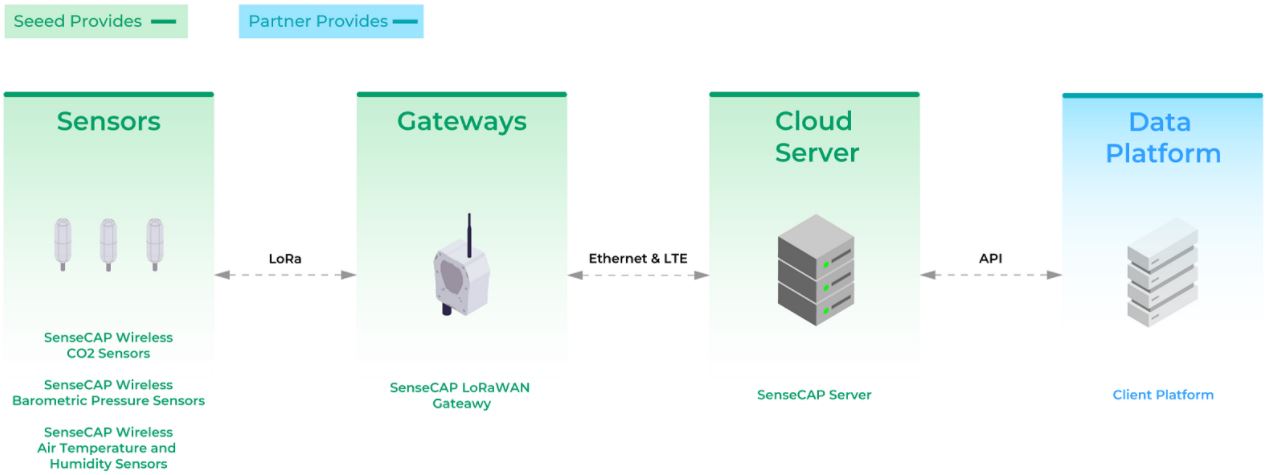
Figure 5. System Deployment Diagram of Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse
Which SDGs Are Relevant?
Among all the 17 SDGs, Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse Project is deeply connected with 4 SDGs (Figure 6): SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production); SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-Being); SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure), and; SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).

Figure 6. Targeted SDGs of Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse Project (UN, 2016)
With respect to the 4 SDGs shown above, it is necessary to highlight SDG 12, as it is the goal that is most directly influenced by Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse project. According to the UN’s (n.d.) statistics, 1.3 billion tons (⅓ of all food produced globally, value of US$ 1 trillion) of food is wasted annually, which ends up going bad due to poor management of transportation, warehouse, and location. Therefore, SDG 12 emphasizes efficient supply chain management, smart resource management, food waste management, and global food security for a sustainable economy (UNDP, n.d.).
Reflecting back on the project, utilizing our SenseCAP is contributing to this goal by lowering the rate of potential food wastes from mismanagement of supply chains, as well as by saving energy costs arising from various situations. When we pay a closer attention to SDG 12’s detailed targets (UN, 2015), it is easy to notice that open tech tools can make a huge contribution on downsizing per capita global food waste at retail level, food losses after the harvest, and in supply chains (Target 12.3); preventing waste generation (Target 12.5) using IIoT solution, and; helping traditional industries like the food sector to adopt sustainable monitoring mechanism (Target 12.6).
To summarize, Baoneng Cold Chain Warehouse project is an exemplary case in point, which demonstrates how our SenseCAP series is enabling food industry players to manage their products intelligently and safely to reduce time, resources, and wastes. This project tells us that we can always start small, and see how our small efforts can be summed up to become a big influence on multiple SDGs for the better version of ourselves, industries, and open IIoT solutions. After all, a cultured person is an artist, an artist in our fast-approaching sustainable world. 😉
About Author
Ye Seong SHIN
Sustainability and CSR Manager at Seeed Studio
。
Jointly organize/participate in multi-stakeholder projects/platforms/events/webinars/workshops/hackathons/etc. to accelerate SDGs with local communities and open tech anywhere in the world by connecting with Ye Seong SHIN today on LinkedIn.
。
Seeed Studio is the IoT and AI solution provider for all types of traditional industries’ sustainable digitalization. Since its establishment in 2008, Seeed Studio’s technological products and customization services are used for smart agriculture, smart cities, smart environmental monitoring, smart animal farming, smart aquaculture, meteorological monitoring, STEAM education, and all types of emerging scenarios enabled by the Industry 4.0. With the company’s mission to “Empower Everyone to Achieve Their Digital Transformation Goals” (which shares similar values with SDGs’ Motto of “Leave No One Behind”), Seeed Studio is devoted to using open source technologies for accelerating SDGs with multi-stakeholders from UN agencies, academia, companies, CSOs, governments, public/private organizations, and so on. This is why, Seeed Studio also founded “Chaihuo Maker Space”, and started China’s first Maker Movement by annually organizing “Maker Faire Shenzhen”.