What Is LoRaWAN?A Simple Guide for Starters
In the world of IoT (Internet of Things), LoRaWAN stands out as a key technology for enabling long-range, low-power communication between devices. Whether you’re building smart farms, smart cities, or tracking assets across a large area, LoRaWAN offers a cost-effective and scalable solution.
1. What Are LoRa and LoRaWAN?
- LoRa stands for “Long Range”,and it refers to a wireless modulation technology developed to support extremely low power consumption while transmitting data over long distances.
- LoRaWAN means “LoRa Wide Area Network”, which is the communication protocol built on top of LoRa.
- In simple terms:
LoRa is the physical layer — it handles radio signal transmission.
LoRaWAN is the network layer — it manages how devices communicate and exchange data.
LoRaWAN enables low power, long range, and low data rate communication — ideal for sensors and devices that need to send small bits of data periodically.

2. How Does LoRaWAN Work?
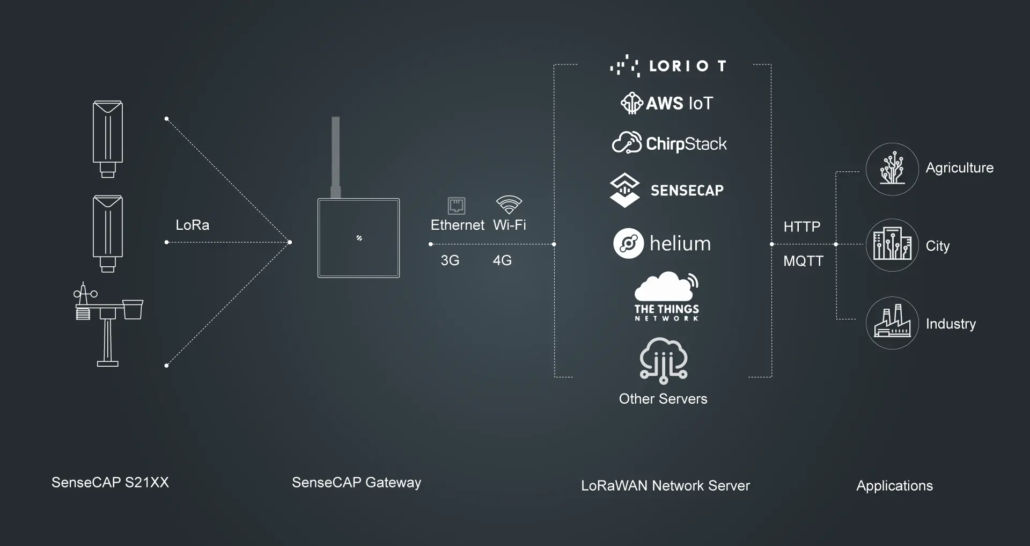
The LoRaWAN architecture consists of four main parts:
End Devices
These are sensors or devices that collect data and transmit it using the LoRa protocol. Common examples include temperature and humidity sensors, air quality monitors, water meters, smoke detectors, and weather stations. These devices are usually battery-powered and optimized for low-frequency data transmission.
LoRaWAN Gateways
Gateways act like bridges. They collect data from multiple end devices and forward it to cloud servers via the internet. In farms, gateways are often installed on tall buildings, rooftops, or communication towers to cover larger fields — up to 10 km or more in open areas.
Network Server
This server manages the LoRaWAN network. It removes duplicate packets, handles device authentication, and ensures data routing to the right application.
Application Server
The final destination for data. It can be a dashboard, cloud platform, or third-party app that visualizes or triggers actions based on the received sensor data.
3. Key Features and Benefits of LoRaWAN
Keywords: lorawan range, lorawan frequency
LoRaWAN is purpose-built for IoT scenarios that require long-distance communication, minimal data usage, and energy efficiency.
Long-Range Communication
- Urban environments: 2–5 kilometers
- Rural or line-of-sight conditions: up to 10–15 kilometers or more
Low Power Consumption
- End devices can operate for 5 to 10 years on a single battery due to the low-duty-cycle communication.
Free-to-Use Frequencies
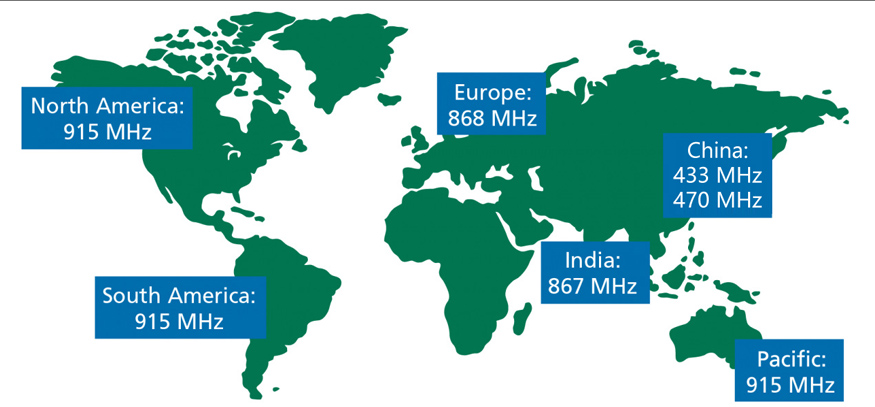
LoRaWAN operates in license-free ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) frequency bands, which vary by region:
- Europe: 868 MHz (EU868)
- North America: 915 MHz (US915)
- Australia & New Zealand: 915–928 MHz (AU915)
- Japan: 920–928 MHz (JP920)
- South Korea: 920–923 MHz (KR920)
- China: 470–510 MHz (CN470)
- India: 865–867 MHz (IN865)
- Canada: 902–928 MHz (US915, same as USA)
- Southeast Asia (e.g., Singapore, Malaysia): Usually 923–925 MHz (AS923)
Note: The AS923 frequency plan is used in several Asia-Pacific countries, including Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Taiwan, and parts of the Middle East. Always check local regulations before deploying.
High Scalability
- A single gateway can handle thousands of devices, making LoRaWAN suitable for city-scale deployments and nationwide coverage when using dense networks.
4. Real-World Applications of LoRaWAN
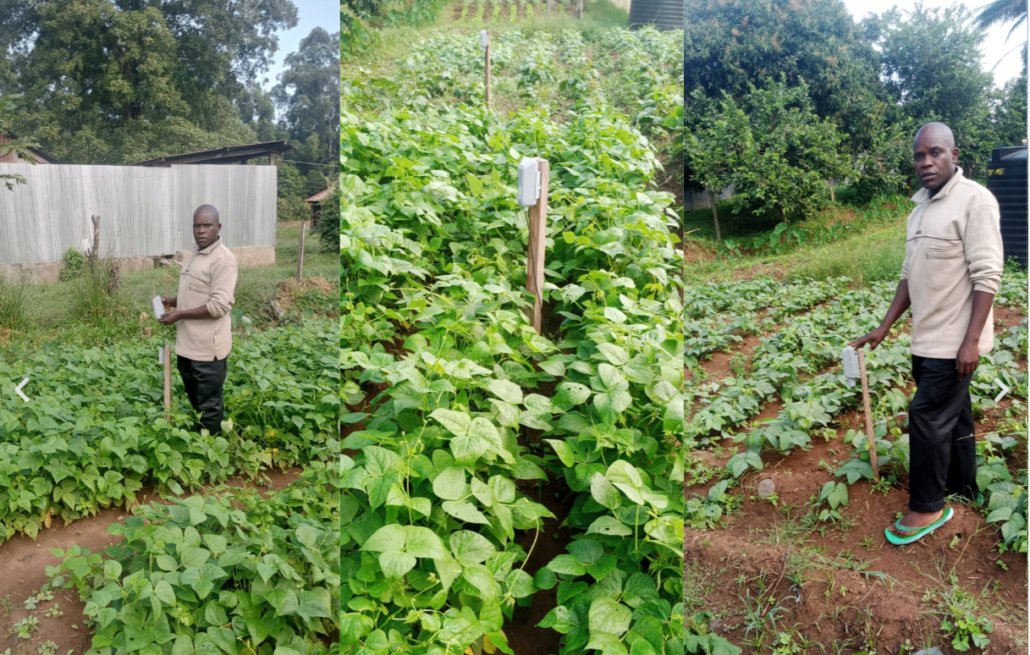
In Kenya, a smart agriculture project led by One Planet Education Network and Mabanga Training Center uses LoRaWAN sensors to collect real-time soil and air data. This helps farmers make data-driven decisions, such as rotating crops and reducing tillage, leading to improved soil health and higher yields—all without relying on costly internet access.

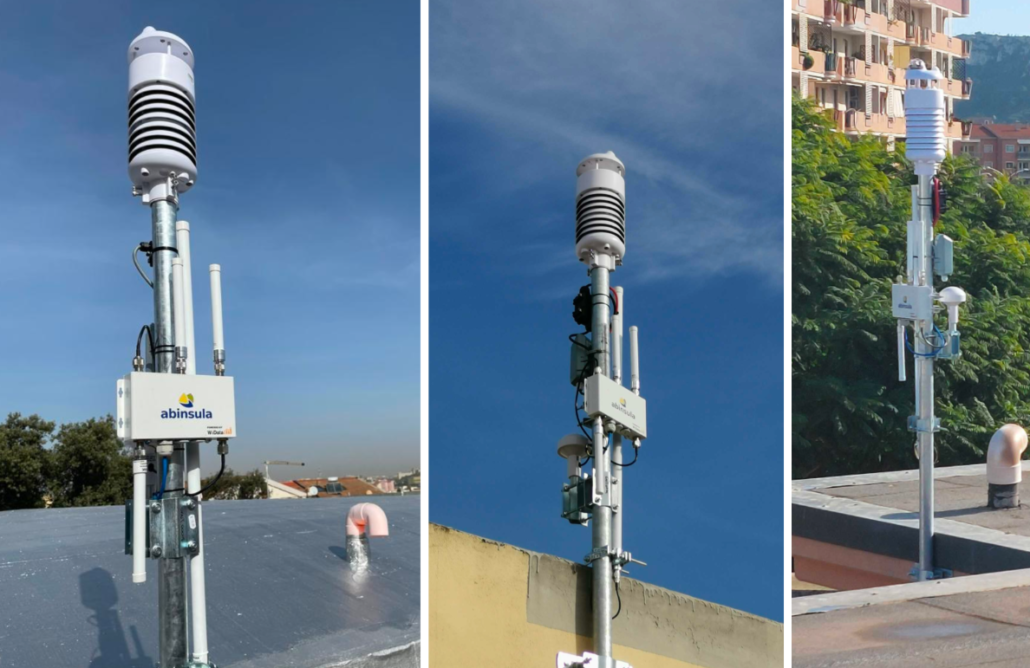
In Italy’s Cagliari, a smart city initiative, more than 500 SenseCAP LoRaWAN sensors have been deployed across 300 locations to monitor urban heat islands. The collected temperature and environmental data supports city planners in redesigning building surfaces and adding green infrastructure to reduce localized heat.

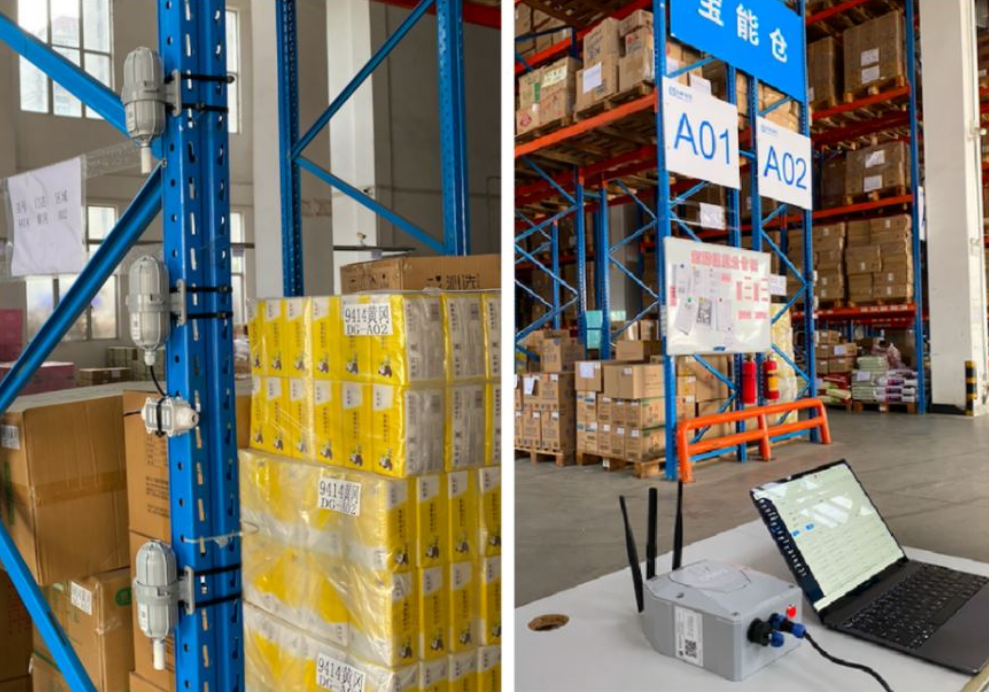
In Shenzhen, China, a cold-chain warehouse implemented an Asset tracking solution using Seeed Studio’s LoRaWAN sensors. These devices monitor temperature and humidity conditions in real time, ensuring food safety and improving traceability throughout the supply chain.

5. LoRaWAN vs NB-IoT: Which One Should You Choose?
| Feature | LoRaWAN | NB-IoT |
| Coverage | Up to 15 km | Up to 10 km |
| Power Consumption | Very low (5–10 years battery) | Moderate (2–5 years battery) |
| Network | Public or private (self-hosted) | Cellular operator required |
| Latency | Higher (seconds) | Lower (ms to seconds) |
| Best For | Agriculture, remote sensors | Smart meters, industrial use |
LoRaWAN is ideal for projects that require flexibility, autonomy, or operate in areas without cellular coverage. NB-IoT is better for applications where strong cellular infrastructure is already in place and lower latency is critical.
6. Public vs Private LoRaWAN Networks
Public Networks
- The Things Network (TTN): A community-powered, open LoRaWAN network. Great for prototyping and collaborative projects. No server hosting required.
- Helium: A decentralized network that rewards users for hosting gateways with cryptocurrency. It has quickly become one of the largest public LoRaWAN networks.
For instance, WeatherXM uses Helium-compatible weather stations (like SenseCAP M4 Square with H2 WeatherXM device) to collect global weather data and reward contributors.

Private Networks
You can build your own LoRaWAN infrastructure using devices like the SenseCAP M2 gateway and open-source software such as ChirpStack. This gives you:
- Complete data ownership
- More security and control
- Customization for industrial or sensitive deployments
However, it requires more technical knowledge and maintenance.
7. Building a LoRaWAN Network: Recommended Gateways
To get started with LoRaWAN, you need a reliable gateway. Here are two trusted options from Seeed Studio:
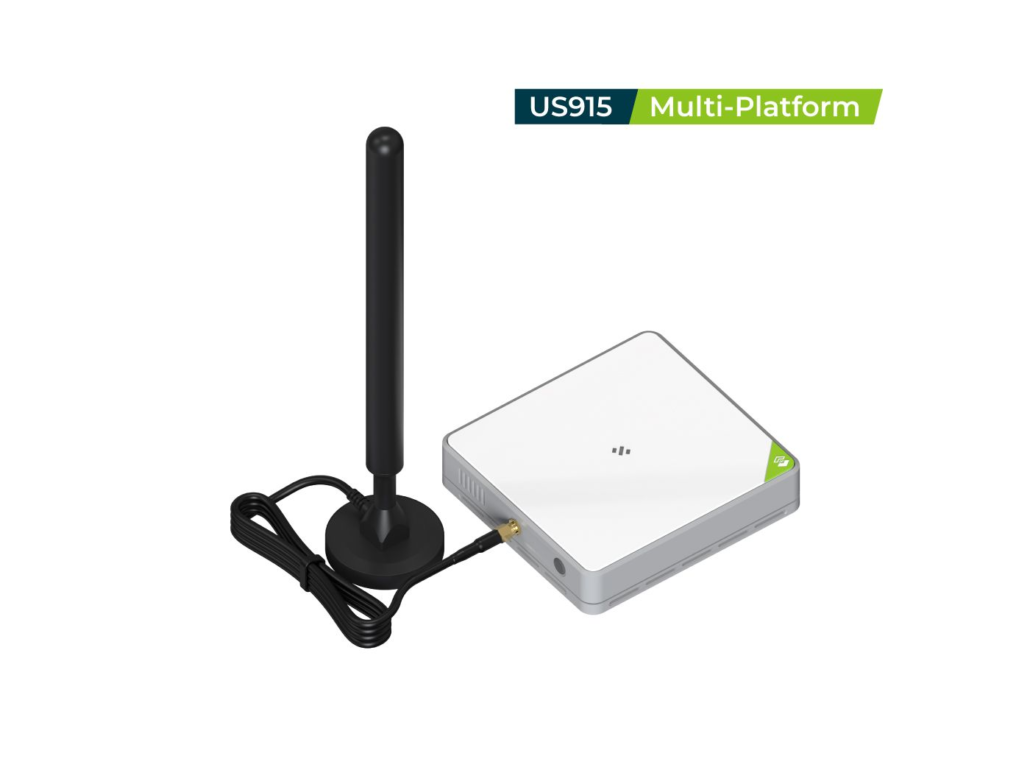
Indoor Option: SenseCAP M2 Gateway
- Multi-protocol support (Helium, TTN, ChirpStack)
- Easy to configure and suitable for testing, labs, and indoor projects
- Available in multiple frequency bands (EU868, US915, AS923)

Outdoor Option: SenseCAP Outdoor Gateway with 4G
- Rugged, IP66-rated enclosure
- Supports 4G LTE, Ethernet
- Ideal for smart farming, urban deployments, or remote sites
Both options are highly compatible with public and private network setups.

8. LoRaWAN Coverage Maps and Developer Communities
Lorawan Maps
Before deploying, it’s useful to check LoRaWAN network coverage in your area:
- Helium Explorer : Displays real-time global gateway locations and signal strength for the Helium network.
- TTN Coverage: Shows community-contributed coverage data for
- SkyNet IoT coverage map: Uses GPS data collected by the SenseCAP T1000 tracker to visualize actual LoRaWAN signal coverage across different environments—ideal for verifying connectivity before deployment.
Joining the LoRaWAN ecosystem also opens doors to global developer communities, helpful resources, and active forums.