How Far Can BLE and LoRaWAN Signals Reach?
The reliability of every safety alert depends on how far and how clearly signals can travel. Some of our readers have also asked about Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Low Power Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) signal range after our previous post on how both work together. In short, BLE handles precise, short-range detection, while LoRaWAN ensures data and alerts are transmitted across a larger area. Together, they create a well-connected network, from room-level positioning to building-wide monitoring.
BLE Beacon Signal Range
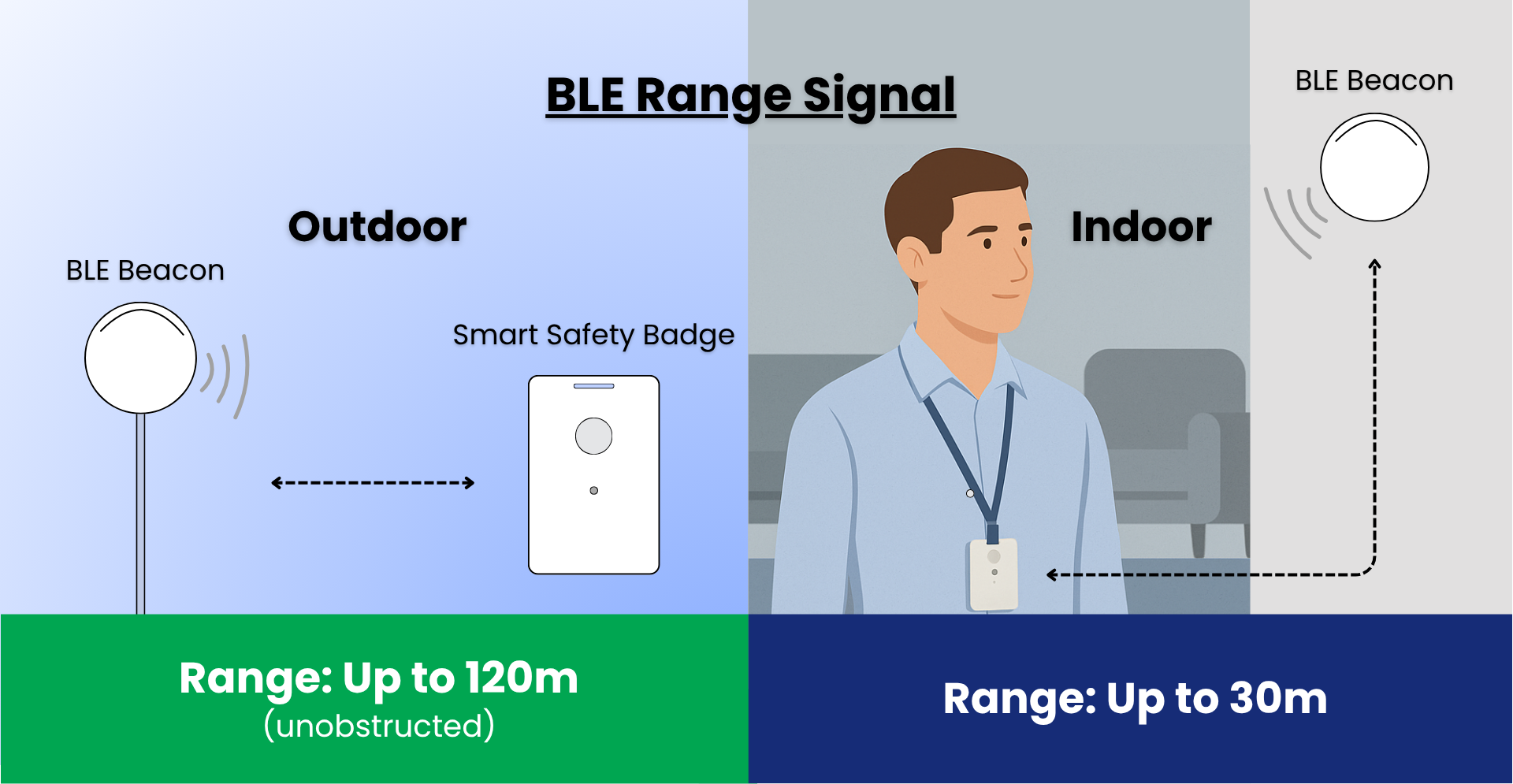
In real-world environments, BLE beacons are best suited for short-range indoor positioning. Typically, their effective range is 10-30 meters indoors, depending on the building layout and materials. In open spaces, this can extend up to 120 meters, but obstacles like walls, metal structures, or human bodies can significantly reduce signal coverage and positioning accuracy. To maintain stable performace, it’s recommended to deploy multiple beacons in areas with clear line-of-sight.
Several factors affect BLE range:
- Physical Barriers: Concrete walls, metal doors, furniture, water—even people—can weaken BLE signals. Different materials cause different levels of attenuation: wood and glass produce low signal loss, brick or marble cause medium attenuation, heavier materials like concrete or plaster lead to high signal loss, and metals or water cause extremely high signal absorption. To better understand how different materials affect BLE performance, you can read this in-depth explanation.
- Interference: BLE operates on the 2.4GHz and uses frequency hopping to reduce interference, but overlapping signals from Wi-Fi routers, microwave ovens, or other 2.4 GHz devices can still cause slight disruptions and reduce effective range in busy wireless environments. Other environmental noise, such as radio frequency interference, can also affect the clarity and strength of Bluetooth signals.
- Power Settings: BLE beacons can be configured with different transmit power levels. Higher power extends signal range but drains the battery life faster. Finding the right balance ensures sufficient coverage while maintaining long battery life for efficient coverage, low-maintenance operation.
While BLE excels in short-range precision, it relies on LoRaWAN to carry those signals further — extending coverage beyond individual rooms or zones.
LoRaWAN Gateway Signal Range
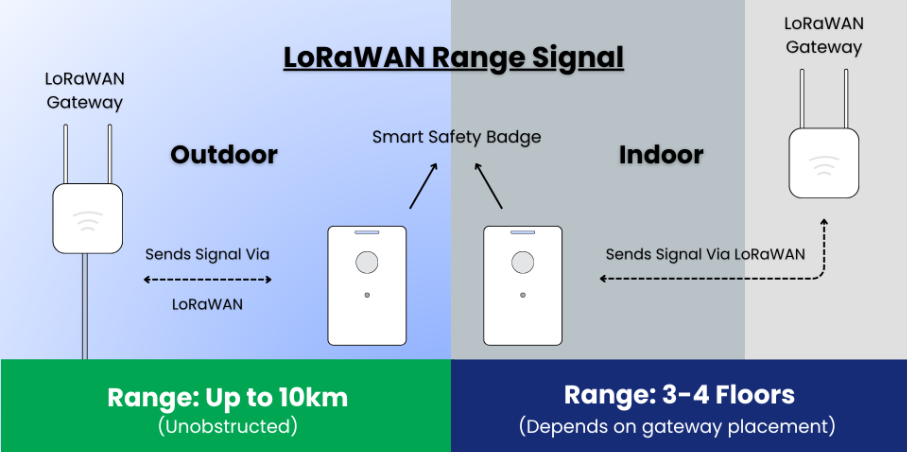
LoRaWAN gateways transmit data and alerts from badges to the monitoring platform over a long-range, low-power network, extending communication across buildings and campuses. In open outdoor areas, a gateway can cover up to 10 kilometers, while indoors the range typically reaches 3-4 floors, depending on the building’s layout and construction materials.
Several factors affect LoRaWAN range:
- Interference: Operating in sub-GHz frequencies (868/915 MHz), LoRaWAN experiences less interference than Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. However, signals can still be affected by building materials and environmental conditions. Dense materials such as concrete, brick, and metal absorb or reflect signals, reducing range; each wall or floor can cause 10–30 dB of signal loss. Moisture, moving people, and electromagnetic noise from machinery can also introduce additional interference.
- Antenna Design & Placement: Gateways placed higher or in open areas offer stronger coverage. Antenna gain plays a role too, higher gain increases range horizontally but reduces vertical reach, which makes moderate omni-directional antennas work best indoors. Gateways don’t need to be near the BLE beacon; they simply need to stay within LoRa range of the badges.
- Network Density: Using multiple gateways enhances coverage and reliability. In complex indoor buildings, overlapping gateway zones ensure thatbadge data is always received by at least one gateway and sent to the monitoring system. If one gateway goes offline, others can automatically take over receiving the badge’s data, maintaining a robust and uninterrupted network.
How BLE and LoRaWAN Work Together
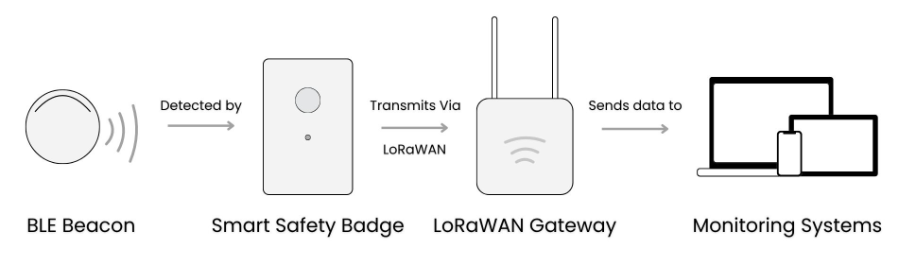
BLE and LoRaWAN work together to bridge short- and long-distance communication. BLE beacons installed across a site provide accurate indoor positioning by transmitting unique identifiers (MAC addresses and RSSI values). When the Smart Safety Badge’s panic button is pressed, it detects nearby BLE signals and sends the data via LoRaWAN gateways for a long-range transmission. LoRaWAN ensures alerts and location data reach the monitoring systems quickly and without interruption, even in dense and multi-floor buildings. Together, BLE provides precision, while LoRaWAN guarantees coverage and reliability.
For deeper comparison of how BLE and LoRaWAN perform against other tracking methods like GPS, Wi-Fi, and UWB, check our previous article on Why BLE + LoRaWAN is the Best Indoor Safety Tracking.
Seeed’s Complete BLE + LoRaWAN Ecosystem
Seeed provides a full, ready-to-deploy hardware ecosystem that includes BLE beacons, LoRaWAN gateways, and the Smart Safety Badge, all designed to work seamlessly. Unified hardware and firmware help solution providers deploy reliable safety networks faster more efficiently.
Seeed also supports extensive customisation, from trigger logic and firmware integration to hardware branding and power options. All products are certified for major regions (FCC, CE, TELEC, SRRC), making global deployment streamlined and compliant.
Discover how Seeed can support your custom deployment — from hardware integration to firmware customization — with a complete BLE + LoRaWAN ecosystem ready for any environment.