An Introduction of Long Range and LoRaWAN Technology
LoRa is a long-range and lower-power wireless communication system providing attractive features that are critical for application in Industrial IoT.
Introduction of Long Rand
What is LoRa?
LoRa is the abstract of Long Range. It is one of the major long-range and lower-power wireless communication systems developed by Semtech Corporation.
“LoRa® is the physical layer or the wireless modulation utilized to create the long-range communication link… It is based on chirp spread spectrum modulation, which maintains the same low power characteristics as FSK modulation but significantly increases the communication range… LR is the first low-cost implementation for commercial usage.“
Quoted from A technical overview of LR® and LoRaWAN
As it provides an attractive combination of features – super long-range, low-power consumption, multi-usage, minimal cost, and encrypted data transmission – LoRa operated in both public and private networks are able to provide much greater coverage compared with the cellular network.
The long-range and low-power nature of LoRa, therefore, is critical for its application in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) which improves our living standards rapidly. It solves many new challenges in both rural and urban areas around the world, including climate change, pollution, natural disasters, etc. Due to its convenience and profitable attributes, LoRa as a kind of Low-Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN), is widely adopted in transportation, manufacturing, facilities, household appliances, and even wearable devices.
Since there are a lot of (and increasing) needs for IoT devices in different vertical industries, especially for low-power, long-range rote data collection scenarios, LoRa is no doubt one of the most sought-after technologies in the market.
Here at Seeed, we are dedicated to providing best-in-class hardware products to meet various needs. Needless to say, we also have a rich collection of LoRa products ranging from modules to dev boards and to devices, please check out the following for your own application needs.
- LoRa Modules
- LoRa Dev Boards & Dev Kits
- LoRa Sensor Nodes (Devices)
- LoRa Gateways
- LoRa Accessories
- Industrial-grade LoRaWAN Products for Outdoor Applications
Technically, how does LoRa function?
Generally, IoT has many technological solutions to transfer data over a network, including LR, NB-IoT, WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and sub-1GHz. But in most cases, long transmission distance and energy conservation can be barely guaranteed simultaneously in wireless communication network systems, because more energy is always needed for longer transmission distance. Thus, LR which can ensure both long-range and low-power is the most optimal choice in situations where transmitting a comparatively small amount of data over a long distance is needed.
To help you establish a direct and basic overview of the application & features of LR, this diagram below shows you the comparison between LR and many other commonly used wireless network technologies.
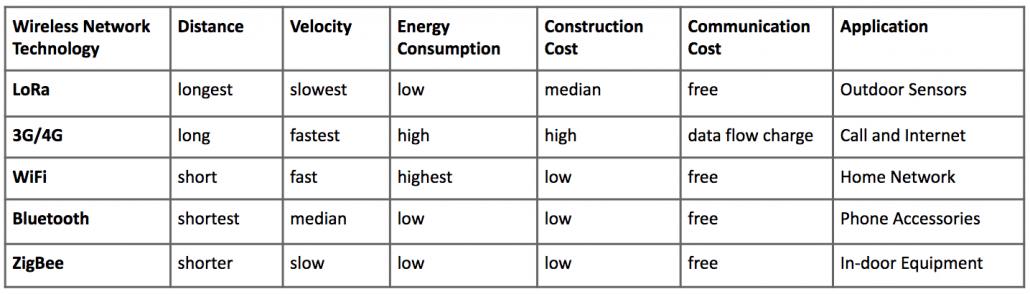
So how does LoRa solve the contradiction between energy and distance while guaranteeing high efficiency?
Technically, LoRa encodes information by using frequency chirps with a linear variation of frequency. According to A Study of LoRa edited by Dongkyun Kim, the frequency offset between the transmitter and the receiver can reach 20% of the bandwidth without impacting decoding performance. This largely reduces the price of LoRa transmitters but creates a sensitivity of the order of -130dBm. At the same time, LoRa improves the sensibility and the anti-interference ability of receivers by generating the Forward Error-correction code (FECs) that corrects errors from the environment. Therefore, compared with traditional modulation schemes like Frequency-Shift Keying (FSK) which requires a Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) to 8dB, LR only needs an SNR of -20dB. As well, the payload of each transmission can range from 2-255 octets and the data rate can reach up to 50 Kbps when channel aggregation is employed.
What are the pros and cons of LoRa?
To know the characteristics of the technology is critical for determining the possible application. Here we make a list to show you some pros and cons of LR. You can use it as a reference to think of fields that LR suits the most.
Advantages:
- Maximizing transmission distance by adopting a spread spectrum gain. According to LRDeveloper Portal, LR provides communications up to three miles (five kilometers) in urban areas, and up to 10 miles (15 kilometers) or more in rural areas.
- Long lifespan: even if the communication distance has reached 5 km, LR can still maintain its energy-saving nature in a superior way. For example, SenseCAP Wireless Soil Moisture and Temperature Sensor, a Seeed industrial IoT product, can maintain its battery use for more than 6 years if the data upload interval is once per hour.
- Working in the free ISM frequency range, provides a convenient manner for common people to use the network and significantly reduces the cost of network deployment.
Disadvantages:
- Low transmission speed: LR has a comparatively narrower bandwidth and is only suitable for sensor networks.
- Higher price of hardware: as a new product/technology, LR has not been widely applied as cellular does. This slightly boosts the price of LR products.
LoRa VS LoRaWAN
Many consider LoRa and LoRaWAN are the same things, as these two have similar names and are often used together. But the fact is they have distinctive concepts.
LoRa is based on a chirp spread spectrum modulation that supports an ultra-long distance wireless transmission, while LoRaWAN is a set of communication protocols and system architecture designed for LoRa long-distance communication network. In other words, LR is a radio frequency carrier signal based in the physical (PHY) layer that converts the data it receives to signals. And LoRaWAN is a protocol located in the Media Access Control (MAC) layer that promotes the LR signals to wider applications. As well, LR is one of the most commonly used LPWAN, especially in the application of IoT corporations and devices.
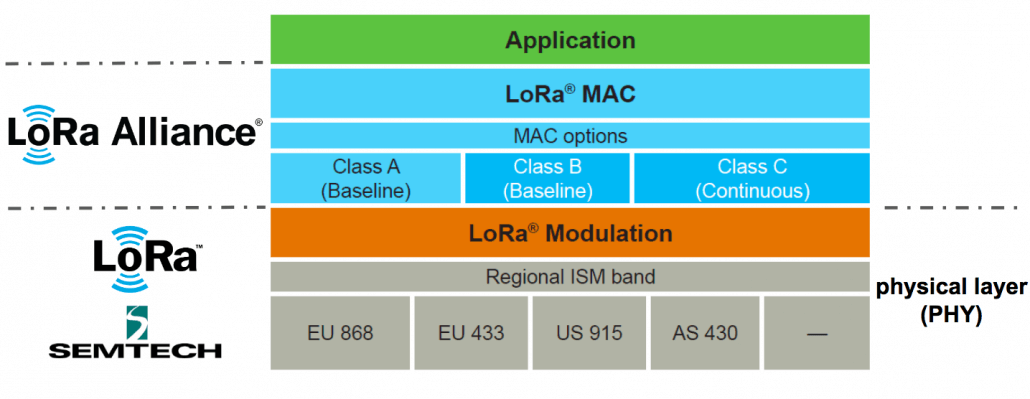
LoRaWAN network architecture
LoRaWAN architecture contains four major parts: end nodes, gateway, network server, and application server. Star topology is adopted between gateways and end nodes, and a single wireless hop is applied to communicate between these two devices. After gathering data, end nodes are able to send messages to multiple gateways at the same time by using LR Radio Frequency (RF). Cellular, WiFi, and or Ethernet Backhaul then help forward the received information in gateways to the network server, the last part which is eligible to finalize the uploading of the packets to the application servers.
Introduction of LoRaWAN
What is LoRaWAN?
According to What Is LoRaWAN:
“LoRaWAN™ defines the communication protocol and system architecture for the network while the LR® physical layer enables the long-range communication link.“
LoRaWAN is an LPWAN standard based on an open-source MAC layer protocol brought out by LR Alliance. It is able to provide local, nationwide, or global network to the battery-powered wireless devices. LoRaWAN specifically focuses on the core demand of IoT, including secure bidirectional communication, accessible mobility, and location identification, etc. Its design has an extreme-easy-to-use mindset, which enables IoT users and developers to develop and deploy the technology flexibly and rapidly.
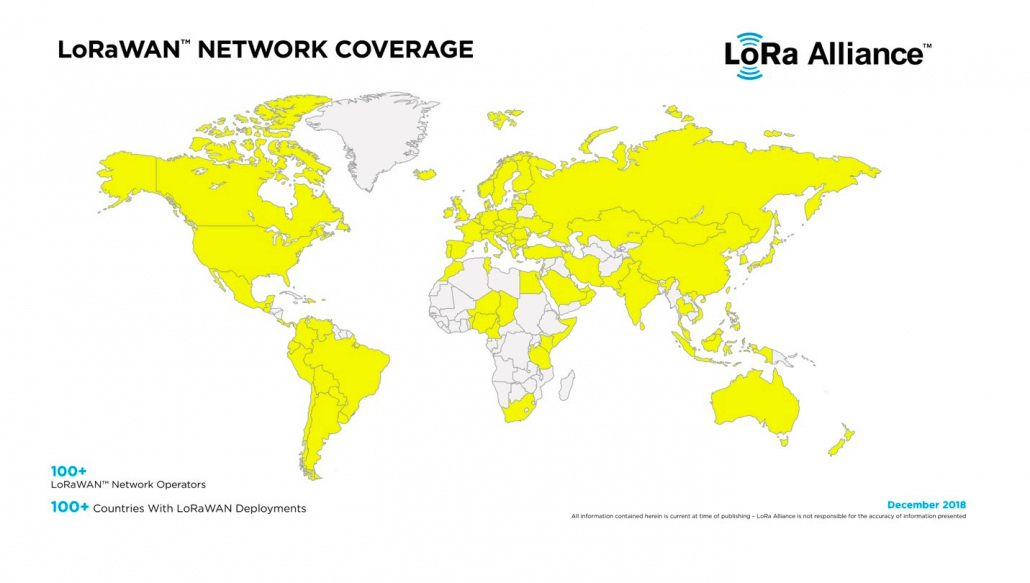
With great reliability and practicality, LoRaWAN has widespread network deployment as there are more than a hundred LoRaWAN network operators around the world, which is clearly shown on the map below.
Star Topology in LoRaWAN
As we mentioned above, LoRaWAN architecture presents as a star topology. Compared with Mesh topology, Star topology can do a better job in maintaining long battery life while enforcing the range of communication.
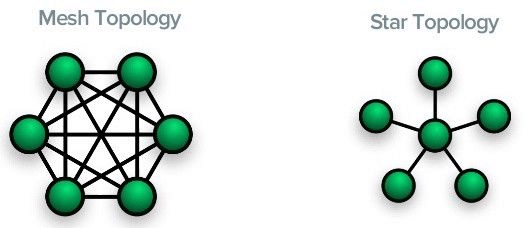
In Star topology structures, messages are transmitted from end nodes to the central servers by using gateways. Gateways act as transparent bridges and only bi-directionally convert the information it receives. Each end node concurrently sends data to multiple gateways and then gateways retransmit data to the network server.
Star topology has three obvious advantages:
- Ensures the reliability of LoRaWAN: no data collision will occur because all devices are asynchronous. When one fails to work properly, the other can still send data to the central server.
- No need for additional communication between gateways, as end nodes can send data to multiple gateways instead.
- Energy-saving: compared with mesh topology (with large communication range but has weak network capacity and short battery lifetime), star topology maximizes both the battery lifespan and the long-distance connectivity.
End Nodes
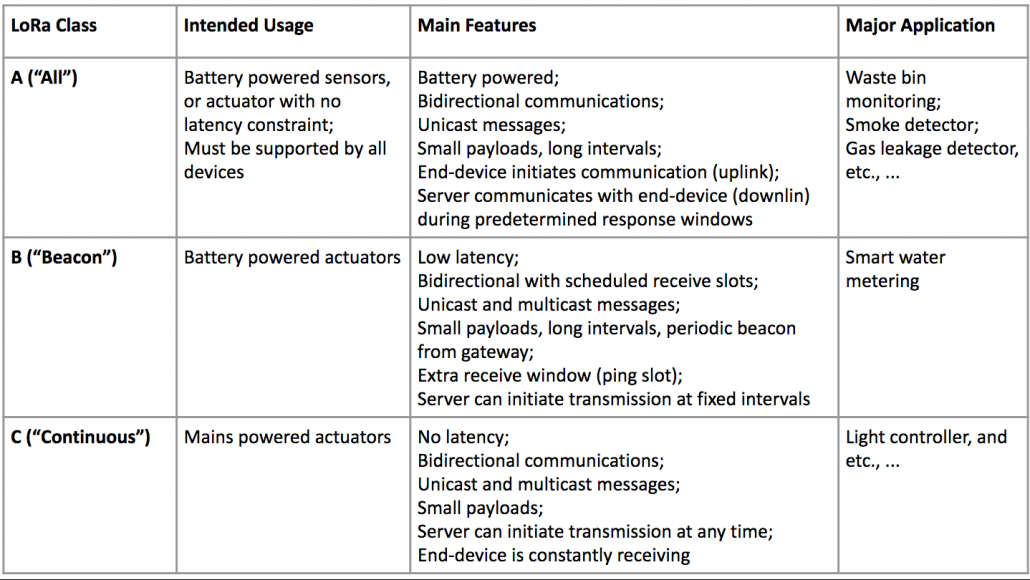
LoRaWAN classifies three types of LR end nodes that serve distinctive requirements and cover almost all kinds of IoT applications. What is LoRaWAN introduces that “The device classes trade off network downlink communication latency versus battery lifetime.” The below chart form shows details of three classes of LR end nodes which can give you a better understanding of the difference of features and the application of the three types of end nodes:
Moreover, all end nodes have to join the network before sending out data. There are two major ways to enact this process: Over-the-Air Activation (OTAA) and Activation by Personalization (ABP).
First, the end node sends “join requests” to the gateway to enact network accessing processes. network server then verifies information including device keys. As long as all information is correct it will send notifications to the end node and start distributing DevAddr. The end nodes and the network server will generate NwkSKey and AppSKey based on information such as AppKey, to encrypt and verify data.
If using ABP to access the network, the operation procedure is more simplified. By directly configuring the three communication parameters – DevAddr, NwkSKey, and AppSKey, the end nodes can directly send out data for application without additional procedures.
LoRa Alliance
As What Is LoRaWAN introduces:
“The LR Alliance® is the fastest growing technology alliance. A non-profit association of more than 500 member companies, committed to enabling large scale deployment of Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) IoT through the development and promotion of the LoRaWAN® open standard.”
Here are some members of LoRa Alliance (updated 2019). Seeed Studio is also one of the LoRa Alliance members that widely develop LoRa technology into industrial IoT products, especially for serving smart agriculture, smart city, and other environmental sensing scenarios.
Application of LoRa technology
Because of its great reliability and outstanding performance, LoRa and LoRaWAN assist more IoT products to contribute to the establishment of smart agriculture, smart cities, and smart industry in recent years
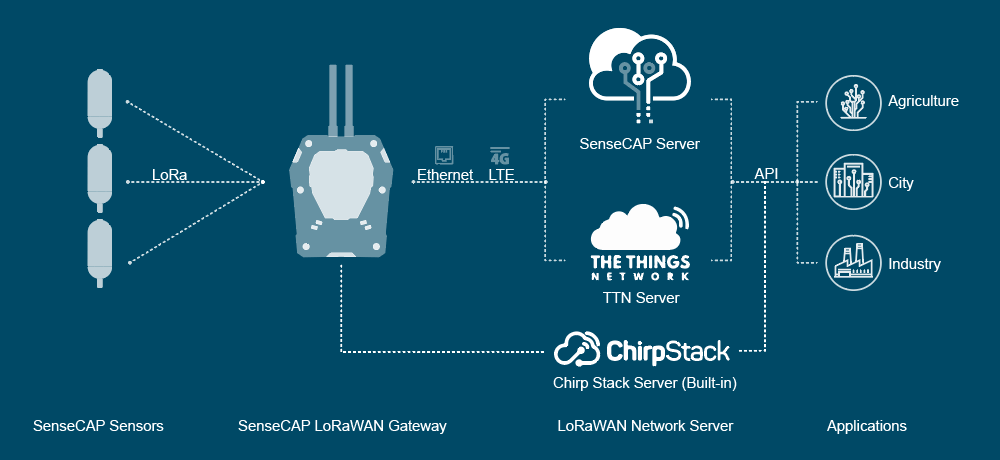
Since 2016, Seeed has started to develop Long Range products, especially open-source hardware to help independent developers around the world turn their novel ideas into creative inventions. At the same time, we realize there is a large and increasing demand for industrial-grade products that can be deployed outdoors and collect data stably and wirelessly for long-term use. Therefore, in 2018, we began to invest in developing Industrial IoT products. The SenseCAP LoRaWAN series is one of the most popular Industrial LR IoT products. It is suitable for applications in a wide range of fields, including outdoor farming such as tea growing on high mountains, fruits & vegetable cultivation in greenhouses, different categories of husbandry, environmental monitoring, and weather stations, just to name a few.
Particularly, if there is no LoRaWAN public network available in your area or if the existing public network does not meet your requirements, you have the option to build your own private LoRaWAN network using the SenseCAP Multi-Platform LoRaWAN Indoor Gateway. Compared to public LoRaWAN networks, private networks allow users to have full control over the network scope, security, and data management.
We also provide SenseCAP LoRaWAN Starter kit tailored for beginners who are exploring LoRaWAN. This kit includes a SenseCAP M2 Multi-Platform LoRaWAN Indoor Gateway, XIAO ESP32-S3, Grove-Wio-E5, and two Grove sensors. It is specifically designed to facilitate the learning process and experimentation with LoRaWAN.

Here at Seeed, we are continuously developing Long Range products to meet different application needs. We are looking forward to cooperating with system integrators, technology providers, and other partners in making LR technologies more accessible to different applications in various industries.
Wio-E5 & Wio-E5-LE (STM32WLE5JC) LoRa Module
For those who want to custom design your LoRa-powered PCBAs, meet our STM32WLE5JC-powered LoRa modules: the Wio-E5 and Wio-E5-LE, which are the world-first combo of LoRa RF and MCU integrated in one single tiny module! Coming with CE, FCC, TELEC certifications, and built-in AT Command, these two modules are production-ready to scale up your LoRa products.

To learn more about Seeed Industrial IoT products, click the link here!
References:
A study of LR: Long Range & Low Power Networks for the Internet of Things: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5038744/
What are LR® and LoRaWAN®?: https://lora-developers.semtech.com/library/tech-papers-and-guides/lora-and-lorawan/
What is LoRaWAN (LoRAWAN White Paper): https://lora-alliance.org/sites/default/files/2018-04/what-is-lorawan.pdf
LoRa 深度解析LR和LoRaWAN的区别: https://blog.csdn.net/
什么是LR?: https://blog.csdn.net/luoyir1997/article/details/80927148
LR几个常见问题总结: https://blog.csdn.net/mycsdn_liruilin/article/details/83049939 by mycsdn_liruilin
LoRaWAN介绍 – LR从业者读这篇就够了: http://blog.csdn.net/iotisan/ by twowinter
Notes
1) The LoRa® Mark and logo are trademarks of Semtech Corporation or its subsidiaries.
2)LoRaWAN® is a mark used under license from the LoRa Alliance®.